Multi-tenant Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems are designed to serve multiple independent entities, called tenants, within a single IAM framework. This architecture is crucial for organizations that want to scale efficiently, allowing each tenant to keep their data and configurations separate while sharing the infrastructure.
These systems allow multiple independent entities, or tenants, to operate within a single IAM framework. They protect each tenant’s data while enabling shared infrastructure, which simplifies administration and enhances collaboration among different organizations.
Benefits of multi-tenant IAM systems
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Cost efficiency | Minimizes operational costs by utilizing shared resources, resulting in a lower total cost of ownership (TCO). |
| Enhanced security | Implements strong access controls and complies with regulations like HIPAA. |
| Scalability | Accommodates the addition of new tenants while adapting to diverse deployment environments. |
| Operational efficiency | Administrators benefit from the ability to manage multiple tenants through a single interface, simplifying operations and minimizing management burdens. |
| Adaptability | Adjusts to changes in legal requirements and organizational policies. |
In this guide, we will examine the architecture of multi-tenant IAM systems, highlight their benefits, and discuss strategies that make them vital for your business..
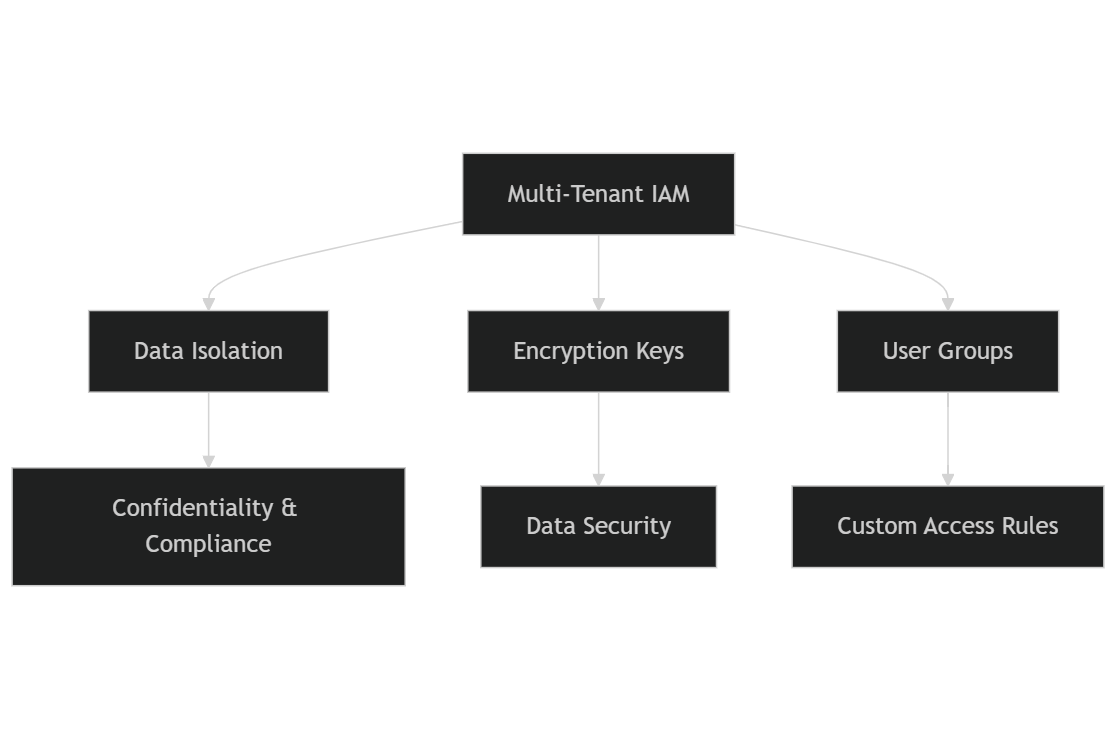
Key components of multi-tenant IAM architecture
- Data isolation: Data isolation is fundamental to multi-tenant architecture, guaranteeing that each tenant’s data stays distinct. This design ensuresconfidentiality and integrity while reducing the risks of unauthorized access, which is essential for compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
- Encryption keys: To improve security, multi-tenant systems use unique encryption keys for each tenant. This approach increases data protection by providing that even if data is accessed, it remains encrypted and unreadable without the correct key, fostering a trustworthy environment for all tenants.
- User groups (tenants): User groups can represent different organizations, departments, or subsidiaries, each with tailored access rules. This capability is vital for customizing security measures to meet specific organizational needs while promoting joint actions among tenants.
Advantages of multi-tenant architecture
- Centralized control: Administrators benefit from the ability to manage multiple tenants through a single interface, simplifying operations and minimizing management burdens.
- Decentralized administration: Although there is centralized oversight, tenants can still manage their specific tasks, which is crucial for organizations with diverse structures.
- Collaboration enablement: This architecture encourages collaboration across different domains and external partners while upholding stringent security measures.
Why multi-tenant IAM reduce operational costs and time?
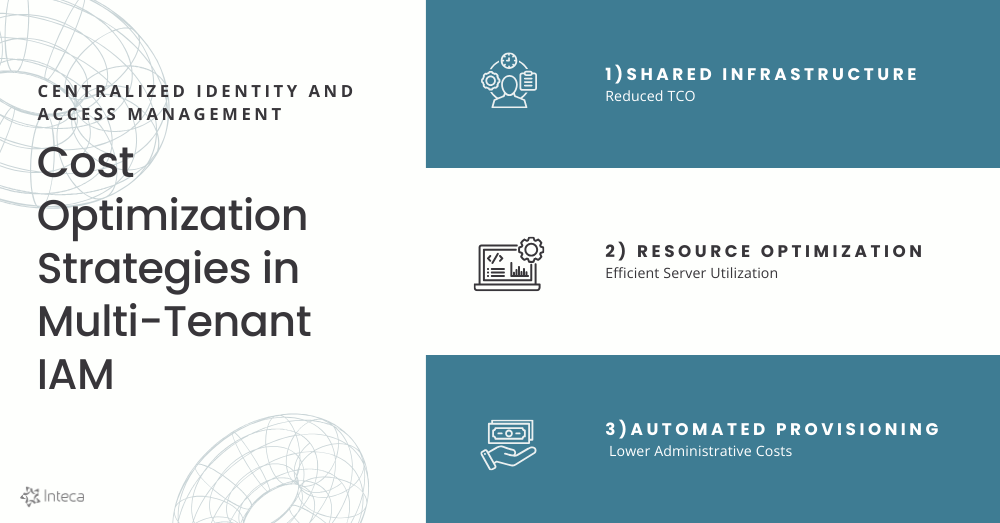
Multi-tenant IAM systems offer substantial cost savings and operational efficiencies that can fundamentally change how organizations function. These systems optimize resource use, allowing companies to lower their total cost of ownership (TCO). By sharing infrastructure, organizations can spend their financial resources more wisely, improving their operations.
-
Cost-effectiveness: Through a shared architecture, multi-tenant IAM systems cut operational costs by enabling organizations to share resources like servers and storage. This collaborative approach reduces the need for multiple software instances, leading to lower capital costs, which is vital for many businesses utilizing a single instance model.
-
Operational efficiency: These systems simplify administration, allowing IT teams to manage user identities and access across different tenants through a single interface. This streamlining saves time and reduces administrative errors, leading to increased productivity in managing authentication and authorization.
-
Automated provisioning: A key feature of multi-tenant IAM solutions is automation, which streamlines the onboarding and offboarding of users. Quickly assigning and revoking access rights boosts security and compliance, allowing IT staff to concentrate on more strategic projects.
-
Resource optimization techniques: Techniques like oversubscription help organizations use resources efficiently without sacrificing performance. This flexibility is crucial for handling changing workloads and leads to additional cost savings.
How multi-tenant IAM increase security?
Organizations should prioritize enhanced security and compliance when using multi-tenant Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems. My experience with various identity and access management projects shows that these systems have robust features that protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with regulatory frameworks.
-
Robust access controls: Multi-tenant IAM systems offer granular access controls that allow organizations to specify precise permissions based on user roles. This level of detail ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data, significantly mitigating the risks associated with unauthorized access.
-
Data integrity and confidentiality: Through the implementation of data isolation techniques, these systems maintain the integrity and confidentiality of each tenant’s data. This separation is not just a best practice; it is essential for compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA, which mandate stringent data protection measures.
-
Security audits and monitoring: Ongoing monitoring and frequent security audits are essential for ensuring effective security measures. These processes help identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with industry standards, fostering trust among customers and stakeholders alike.
-
Compliance regulations: Designed to support a variety of compliance regulations, multi-tenant IAM systems empower organizations to navigate complex legal landscapes with ease. This capability is particularly important in healthcare and finance, where compliance is mandatory and often tied to strict authentication protocols.
-
Sensitive data management: Advanced features like data masking and encryption enable organizations to manage sensitive data effectively. These practices not only enhance privacy but also help organizations comply with data sovereignty regulations, safeguarding user information from potential breaches through robust authentication and authorization mechanisms.
Recent discussions in the industry highlight an urgent need for strong identity management practices. A report from CSO on March 4, 2025, explicitly stated that misconfigured access management systems pose significant security risks to global enterprises. This highlights the need for robust IAM solutions that focus on security and compliance to protect against growing cyber threats.
Scalability of multi-tenant IAM
Multi-tenant Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems offer crucial scalability and flexibility, enabling organizations to manage growth and transformation effectively. Scalability in these systems allows businesses to easily add new tenants and handle changing demands smoothly, which is vital for organizations looking to grow or adapt.
Various deployment environments
Multi-tenant IAM solutions are versatile and can be deployed across various environments, including:
– Public Cloud: This environment enhances the scalability of multi-tenant systems, allowing them to support numerous tenants effectively.
– Private Cloud: Organizations that prioritize data security can benefit from a private cloud setup, which provides dedicated resources to protect sensitive information.
– Hybrid Clouds: This approach offers a strategic blend, enabling organizations to leverage both public and private cloud resources based on specific requirements.
Database multi-tenancy approaches
Implementing various database multi-tenancy strategies is essential for effective data management in IAM systems:
1. Shared Tables: This method lets multiple tenants use the same database tables, making management easier, but it requires careful attention to ensure data isolation for privacy.
2. Separate Schemas: Each tenant operates within its own schema in a shared database, striking a balance between isolation and manageability.
3. Separate Databases: This approach provides the highest level of data isolation, as each tenant has its own database. However, it may complicate management.
Scaling strategies
As companies grow, the demand for effective identity management solutions rises. In my work with clients in identity and access management, I’ve seen that multi-tenant IAM systems employ various strategies to meet the increasing demands for performance and reliability:
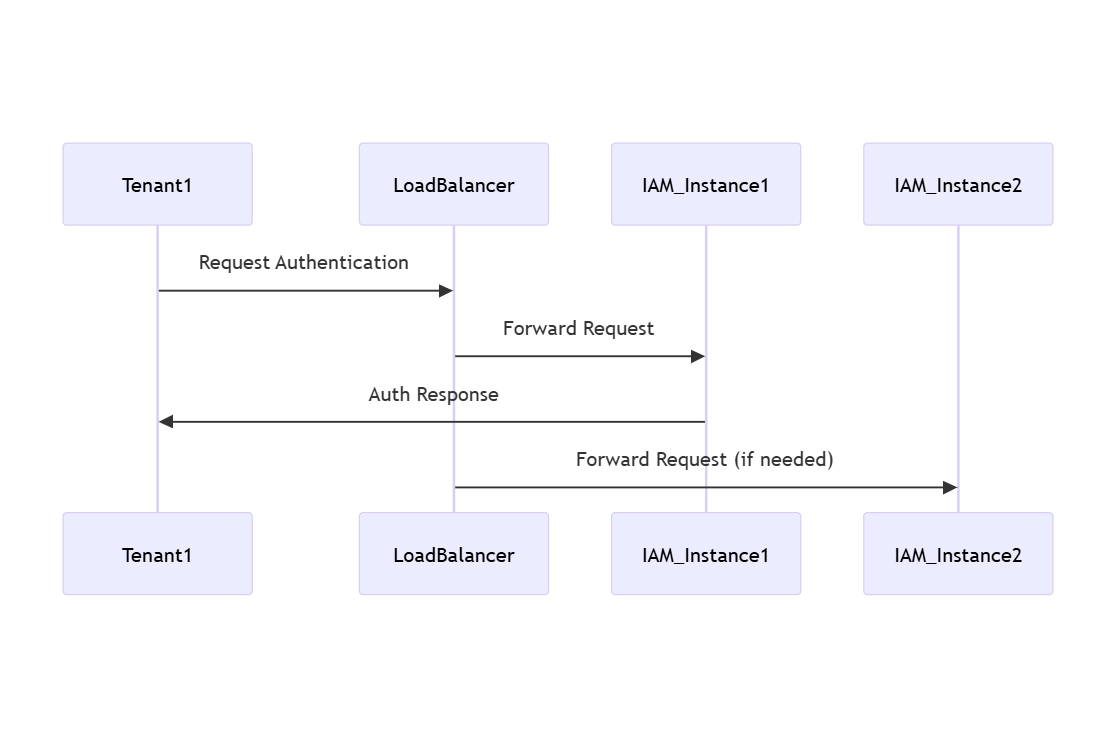
1. Horizontal scaling
Horizontal scaling means adding more service instances to share the workload more evenly. This approach works well in multi-tenant setups, making it easier for companies to add new tenants without sacrificing performance. Deploying multiple IAM instances helps organizations manage user requests and keeps the system responsive.
2. Load balancing
Load balancing helps optimize how resources are used across servers. It directs user traffic to servers with less load, preventing any one server from becoming overwhelmed. This method improves system performance and reliability by lowering the chances of server overload and downtime. Implementing load balancers in multi-tenant IAM solutions contributes to a seamless user experience, even during busy periods.
Interested in Multi-tenant IAM?
3. Resource allocation complexity
Navigating resource management in a multi-tenant system can be intricate, given the diverse needs of different tenants. Effective resource allocation is key to giving each tenant the resources they need based on their usage. Dynamic resource allocation and predictive analytics help organizations optimize resources and keep performance steady for all tenants.
4. Emerging security concerns
Scaling strategies can also introduce new security challenges. As systems become more interconnected, the potential for vulnerabilities increases, necessitating the implementation of robust security measures. Organizations must focus on security measures like encryption, strict access controls, and regular audits to safeguard sensitive data during IAM scaling. By tackling these new security challenges head-on, organizations can grow without compromising data integrity and compliance.
Adaptability of multi-tenancy
Adaptability in multi-tenant Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems enables organizations to swiftly adjust to new legal requirements and internal policies. This agility is crucial in a constantly evolving regulatory landscape, where compliance requirements can change at any moment.
- Regulatory compliance – These systems are designed to easily accommodate new legal frameworks. They include features that allow organizations to quickly adjust access controls and data management practices to meet changing data protection laws.
- User-centric solutions – Focusing on user experience, multi-tenant IAM systems offer tailored access solutions that improve compliance and boost user satisfaction. This focus allows users to navigate the system seamlessly while adhering to necessary security protocols.
A clear example of this adaptability is the Pentagon’s IT agency, which is developing a streamlined identity solution to enhance digital verification and access within military sectors. This initiative reflects a growing trend toward unified and flexible identity management solutions across public and private sectors (Defense One, Feb 2025).
Key takeaways
The advantages of multi-tenant Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems are essential for organizations looking to optimize their identity management. Here are the key takeaways:
- Cost efficiency: Using shared infrastructure can greatly lower operational costs and decrease the total cost of ownership (TCO).
- Enhanced user experience: Streamlined administration and automated processes make it easier for users to navigate the system, leading to higher satisfaction and improved productivity.
- Scalability: These systems can easily add new tenants, allowing for growth without affecting performance.
- Operational efficiency: Centralized control simplifies management tasks, freeing IT teams to concentrate on more important projects instead of day-to-day operations.
Explore how multi-tenant IAM can provide secure and scalable identity management