Identity and Access Management (IAM) is crucial for any organization’s security and operational efficiency. I’ve seen how effectively these systems can manage user identities and permissions, ensuring that individuals only access the resources they need. This approach strengthens security and simplifies operations, which is essential for protecting sensitive data and meeting regulatory requirements. However, while centralized IAM brings many advantages, some organizations still rely on dispersed IAM strategies that introduce hidden costs and risks. This article explores both sides to highlight the true cost of dispersed identity systems.
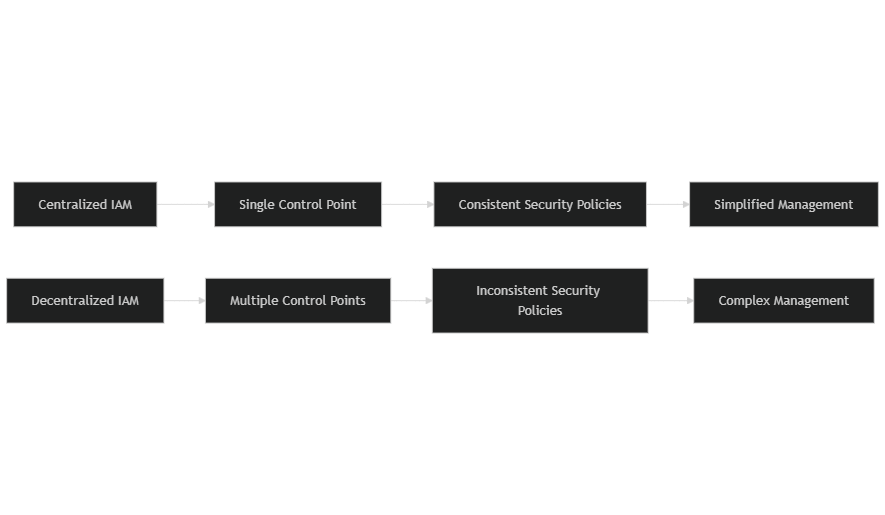
Centralized IAM streamlines identity management by centralizing control, making it easier to enforce security policies and reduce unauthorized access. A single directory supports Single Sign-On (SSO) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), boosting security while minimizing password resets. It also automates user provisioning and de-provisioning, reducing administrative burdens so employees gain quick access to essential tools—vital in dynamic business settings. Additionally, centralized IAM offers clear audit trails to help organizations meet regulatory standards. Nevertheless, the following sections will examine how dispersed IAM often carries hidden costs and challenges.
Risks associated with dispersed IAM systems
Dispersed Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems pose various security risks, compliance challenges, and unexpected costs that organizations must tackle head-on. Based on my experiences with IAM projects, I will outline these risks to provide a clearer understanding.
Security risks
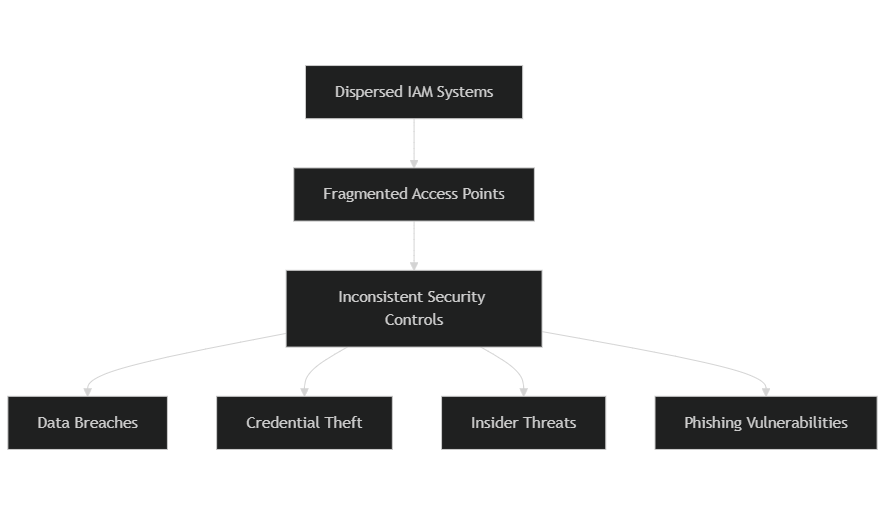
The fragmented nature of dispersed IAM systems can lead to significant security vulnerabilities. Let’s explore some crucial security risks:
- Data breaches
A recent report shows that identity fraud attacks on social media increased by 27% in 2024¹. This trend indicates a greater risk of data breaches for organizations using dispersed IAM systems. When access is scattered, unauthorized entry can lead to substantial data loss and financial ramifications. - Credential theft
With access points and credentials spread across multiple platforms, credential theft becomes a pressing issue. Cybercriminals quickly exploit weaker access controls, gaining unauthorized access to sensitive information when organizations lack a unified approach. - Insider threats
Insider threats are a significant issue, especially when access management is decentralized. Employees with excessive privileges or those who haven’t had their access revoked after leaving the organization can misuse their credentials, resulting in data breaches that could have been avoided. - Phishing resistance
Another concern is the lack of cohesive security training in dispersed setups, which leaves employees vulnerable to phishing attacks. A centralized IAM system can provide consistent training and resources, significantly reducing the risk of falling victim to such attacks.
Compliance challenges
Compliance can be a minefield for organizations operating with dispersed IAM. Here are the hurdles they might encounter:
- Regulatory compliance
Keeping up with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS is no small feat. Dispersed IAM systems can complicate compliance efforts, often resulting in inconsistent access controls and incomplete audit trails that could draw scrutiny from regulators. - Access governance
The management of access rights across multiple platforms often creates governance headaches, raising the risk of non-compliance. Organizations must implement robust frameworks for access governance to monitor user permissions effectively. - Privacy concerns
The growth of biometric authentication systems like India’s Aadhaar has raised serious privacy concerns regarding possible misuse of sensitive data². Organizations must ensure that their IAM systems comply with privacy regulations to avoid legal pitfalls.
Central database risks
While centralized IAM systems have their benefits, they also come with their own set of vulnerabilities. Here are a couple of risks associated with central databases:
- Single point of failure
Centralized systems are often major targets for cyberattacks. A successful breach could allow attackers to access all user data, resulting in severe financial and reputational damage to the organization. - Scalability issues
As organizations expand, their centralized IAM must keep pace. Systems not designed to scale may struggle with increased user demands and diverse access needs, resulting in performance bottlenecks.
In conclusion, while dispersed IAM systems may offer flexibility, they introduce significant risks that organizations must manage with care. A centralized IAM strategy enhances security and simplifies compliance efforts, ultimately safeguarding assets and reducing unexpected expenses.
IAM risk assessments
Framework for risk assessment
Conducting thorough risk assessments pinpoints vulnerabilities and quantifies risks in identity management. Here’s how I approach this process:
- Identifying vulnerabilities
– Start by mapping out all the IAM components, which include user roles, access points, and any third-party integrations. This provides a comprehensive understanding of your system.
– Review access permissions carefully and identify excessive privileges or misconfigurations that could risk your organization.
– Use automated tools to scan for vulnerabilities, such as outdated software and weak password policies, allowing you to address these issues proactively. - Assessing impact and likelihood
– Next, evaluate how the identified vulnerabilities could impact your organization’s operations, data integrity, and compliance stance. Recognizing the potential impact of these vulnerabilities is essential.
– Employ both qualitative and quantitative methods to assess the likelihood of each risk based on historical data and industry benchmarks.
| Vulnerability type | Impact level | Likelihood level |
|---|---|---|
| Excessive user privileges | High | Medium |
| Weak password policies | Medium | High |
| Third-party integration gaps | High | Low |
Tools and techniques
Effective IAM risk assessments require the right tools and techniques. Here’s what I recommend:
- Regular assessments and audits
- Create a regular schedule for risk assessments and audits to consistently monitor your IAM systems. Regular checks can catch issues before they escalate.
- Automated compliance tools can streamline the auditing process, making it easier to identify discrepancies and risks quickly.
- Insider threat detection solutions
- Implement solutions that monitor user behavior and access patterns to detect potential insider threats early.
- Use analytics tools with machine learning to identify anomalies in user activity, which can help in detecting misuse or compromised accounts.
Following this structured framework and using these tools enables organizations to gain a comprehensive understanding of their IAM risks, which supports effective decision-making for centralized IAM strategies.
Best practices for conducting IAM risk assessments
Effective IAM risk assessments require adherence to best practices. Here are the practical steps to follow:
Establish a clear scope
- Define assessment boundaries
– Map out which systems, applications, and data will be included in your assessment. This clarity enables a focused and streamlined evaluation process.
– Additionally, consider regulatory and compliance requirements specific to your organization to ensure comprehensive coverage. - Engage stakeholders
– Bring in key stakeholders from IT, security, and business units early on. Their diverse insights can foster collaboration and enhance the assessment process since IAM impacts various functions within the organization.
Utilize comprehensive methodologies
- Risk assessment frameworks
- Adopting established frameworks such as NIST or ISO 27001 is essential. These frameworks provide a structured approach to identifying and mitigating risks effectively.
- Customize these frameworks to fit the unique context and needs of your organization.
- Quantitative and qualitative analysis
- Using both quantitative (like financial impact) and qualitative (such as reputational damage) assessments provides a well-rounded view of the risks involved.
- Implement scoring systems to prioritize risks based on their likelihood and impact, which aids in making informed decisions.
Continuous improvement
- Regular reviews
- Regularly schedule reviews of your IAM risk assessments. This allows you to adapt to changes in technology, threats, and business operations effectively.
- Establish a feedback loop that incorporates lessons learned from previous assessments to refine future evaluations.
- Training and awareness
- Conduct training sessions for employees, emphasizing IAM best practices and the critical importance of security measures. This proactive approach helps in identifying potential risks at an early stage.
| Best practice | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Clear scope | Define boundaries and engage stakeholders | Focused assessments |
| Comprehensive methodology | Utilize frameworks and dual analysis | Holistic risk understanding |
| Continuous improvement | Regular reviews and training sessions | Adaptability and enhanced security |
Implementing these best practices enables organizations to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of their IAM risk assessments. This approach effectively identifies vulnerabilities and facilitates informed decision-making for a centralized IAM strategy.
Hidden costs of dispersed IAM
While dispersed Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems can offer certain advantages, they frequently hide significant costs that can negatively affect an organization’s financial health. In my experience with various IAM projects, I have observed how unexpected expenses can accumulate and affect financial performance. It’s crucial for security professionals, CISOs, and project managers to understand these costs when promoting centralized IAM solutions.
Operational efficiency
Scalability issues
As organizations implement more sophisticated identity management systems, they often encounter scalability challenges. Dispersed IAM systems can create significant delays as user demands increase. Utilizing AI-based solutions can help address these challenges and improve identity management efficiency.
Interoperability challenges
Another challenge with dispersed IAM is the difficulty in achieving interoperability, which can increase both integration costs and timelines. When various systems don’t communicate smoothly, organizations might find themselves needing additional middleware or custom integrations, driving up operational expenses that could have been avoided with a more unified approach.
User experience
A fragmented IAM environment can adversely affect user experience, resulting in employee frustration. Juggling multiple passwords or navigating through several interfaces can diminish productivity significantly. This inefficiency often sparks increased help desk calls and dissatisfaction, ultimately affecting overall performance.
Administrative overhead
Cost of misconfigured policies
Misconfigured IAM policies are common issues in dispersed systems. These errors can result in unauthorized access or compliance violations, leading to expensive remediation. Organizations can incur costs of up to $1.5 million annually due to misconfigurations, encompassing fines and lost productivity.
Time and resources for management
The management of several IAM systems often creates significant administrative challenges. Security teams often find themselves bogged down with manual tasks like user provisioning and policy enforcement, which drains resources and diverts focus from more strategic security initiatives. A centralized IAM approach can streamline these processes, allowing teams to channel their energy into higher-value tasks.
| Description | Potential financial impact | |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability issues | Increased costs due to bottlenecks and inefficiencies | Up to 30% increase in operational costs |
| Interoperability challenges | Additional integration costs and time delays | $100,000+ annually |
| Misconfigured policies | Costs associated with unauthorized access and fines | Up to $1.5 million annually |
| Administrative overhead | Resource drain from managing multiple systems | $250,000+ in lost productivity |
In summary, although dispersed IAM systems provide some flexibility, the hidden costs related to operational inefficiencies and administrative overhead can be significant. By transitioning to a centralized IAM solution, organizations can mitigate these costs, enhance their security posture, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Key takeaways
Centralized Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems offer significant benefits that organizations should consider. Here’s a recap of the main points:
Benefits of centralized IAM
- Enhanced security: A centralized IAM framework simplifies security policy enforcement, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data leaks.
- Operational efficiency: Simplifying user provisioning and access management alleviates administrative burdens, improving operational efficiency.
Importance of ongoing risk assessments
- Continuous monitoring: Regular risk assessments are crucial for identifying vulnerabilities and adapting to emerging threats.²
- Compliance assurance: Consistent evaluations support organizations in meeting regulatory standards, safeguarding them from legal penalties.
Need for a proactive IAM strategy
- Strategic planning: A proactive IAM strategy enables organizations to anticipate challenges, implement timely adjustments, and mitigate risks effectively.
- Investment in technology: Embracing advanced IAM solutions like Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and behavioral analytics not only boosts security but also enhances operational performance.
Reference List:
- AU10TIX, https://www.au10tix.com/news/identity-fraud-attacks-on-social-media-2024
- TechCrunch, https://techcrunch.com/2025/02/06/aadhaar-authentication-businesses-privacy-concerns/
- Organizations Face Scalability Challenges with Complex Identity Management Systems – SecurityWeek, https://www.securityweek.com/scalability-challenges-identity-management-systems/
See why Keycloak may be the best choice for your login needs!